FAIRification Process
Data is the fuel for researchers. Owing to a new awareness for transparent and open science processes, they increasingly aim to make the output of the research lifecycle searchable and available to others. The FAIR Principles guide researchers in their efforts of making data findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable.
FAIRification Process
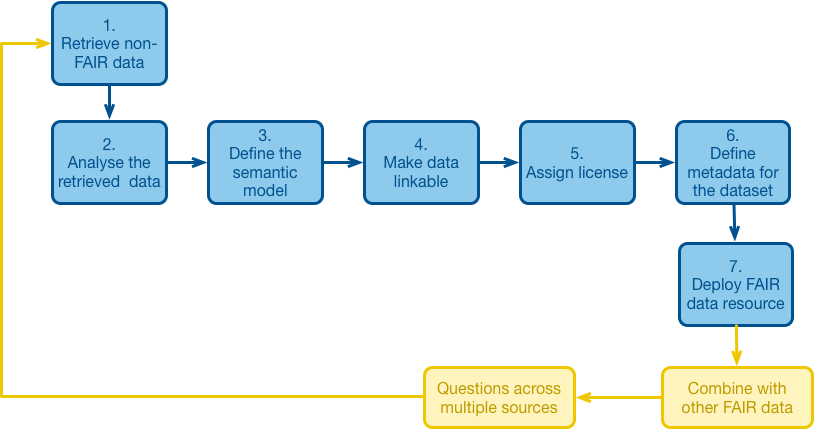
As a provider of a FAIR service or tool, you need to consider the FAIRification process and how to facilitate the process of making data FAIR.
FAIRification Requirements
- Retrieve Non-FAIR Data
- Describe & Analyze Data
- Managing and Sharing Data: Best practices for managing and sharing data
- How to Go FAIR
- Rich Metadata
- Metadata standards
- The Data Documentation Initiative (DDI): Standard for describing the data
- Persistent Identifier
- Persistent identifiers: working level – ANDS: What, why and when to use PID
- Ontology and Semantic model
- 5 Stars Machine Actionability Model: The 5-star model shows importance and benefits of machine-actionability, open data, and semantic modelling
- Data Storage
- CoreTrustSeal Trustworthy Data Repositories Requirements
- Recommendations on certifying services required to enable FAIR within EOSC: An analysis of activities relevant to certification of the services required to enable FAIR research outputs within EOSC
- Data Licenses
- Deploy FAIRed Data
- How to Go FAIR
- Turning FAIR into reality: A survey and analysis of what is needed to implement FAIR. The document provides a set of concrete recommendations and actions for stakeholders in Europe and beyond.
